Tuesday, July 10, 2012
Mechanical (Rotary) Common Questions -1
EPC-School 2012
M for Mechanical
M for Mechanical
Topic - PUMPS, SEALS
1. What is the operating principle of rotodynamic vs
positive displacement pump?
2. What is ‘head’ of a pump?
4. What are the application criteria with respect to
pressure and flow for centrifugal and positive displacement pumps?
5. What are the different types of radial and axial thrust bearings?
6. What are the different types of positive displacement
pumps?
7. What are the different constructions of centrifugal
pumps?
8. What is the advantage of a double volute casing over
single volute?
9. What are the specific requirements needed for a
centrifugal pump used in slurry application?
10. What is cavitation?
11. What are the causes of cavitation?
12. How is axial thrust generated in pump?
13. Why is hydrotest of equipment done?
14. Which API governs centrifugal pumps?
15. What does NPSH mean?
16. How NPSH affects the pump performance?
17. What are NPSHa and NPSHr?
18. What are the affinity laws?
19. What are the different impeller types and their applications?
20. What types of pumps are used for metering application?
21. What are the effects of cavitation?
22. What are normal and rated operating point for a given
pump?
23. What is system resistance? How does system resistance
affect pump operating point?
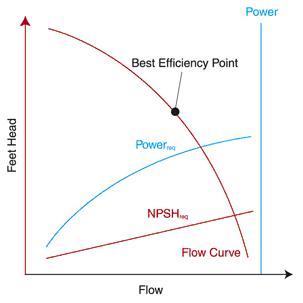
24. Draw a typical performance curve (head Vs Flow) for a
centrifugal pump.
25. Which consumes more energy at same volume flow rate and
differential pressure: lighter or
heavier liquid?
26. What are the different types of sealing mechanism in a
pump? State typical application for each.
27. What are primary and secondary sealing elements in a
mechanical seal?
28. What are the application criteria for single / double (including
tandem) mechanical seals?
29. Which seals are recommended in case of toxic service?
30. List some of the flushing plans
31. What is the function of pumping ring in seal flushing
plans and in which plans it is used?
32. Which buffer/barrier fluid is generally used in seal
flushing plans?
33. Which flushing plan is for inboard seal in high
temperature services?
34. How can we detect failure of flushing plan 23?
35. In flushing plan 53, seal pot pressure alarm is
generated when pressure is increasing or decreasing?
Answers to Above Questions-
1. In positive displacement pumps energy is periodically
added to closed fixed volume fluid resulting in increase in pressure. In
rotodynamic pumps energy is continuously imparted to the liquid with the help
of rotating element.
2. Head of the pump is the energy imparted to the fluid by
the pump equivalent to a height static column of the liquid being pumped
3. Wear rings are used on impellers and on casing on the
suction eye to avoid the recirculation of liquid being pumped and to protect
the impeller or casing from damage due to contact.
4. Centrifugal pumps are used mostly where variable flow and
near uniform discharge pressure is required and reciprocating pumps are used
when constant flow and variable discharge pressure is required. Centrifugal
pumps are used for high flow and low pressure applications while reciprocating
pumps are used for high pressure and low flow applications.
5. Journal bearings & antifriction bearings
6. Positive displacement pumps are classified into rotary
and reciprocating types.
Reciproacating pumps are again classified on the basis of
use of piston ,plunger or diaphragm for compression.
Rotary type is classified as screw type, progressive cavity
type, gear type, vane type, lobe type.
7. Overhung type, Between bearing type, vertically suspended
type
8. Double volute casing design increases the operating range
of pump without much change in radial vibration. In double volute casing the
radial load on the impeller gets balanced whereas in single volute casing radial
load on impeller are balanced for a small range of flow.
9. High wear ring clearances, special materials of
construction, Back vanes to prevent slurry from entering seals
10. The phenomena of vapours entering the pump, formation of
bubbles and subsequent collapse of the bubbles at higher pressure regions is
called cavitation.
11. Cavitation occurs when vapour pressure of pumping liquid
goes higher than pressure of liquid or when vapour enters the pump through
suction line.
12. Impeller (hence pump) is subjected to axial thrust
because a portion of the front wall is exposed to suction pressure (eye)
whereas the whole of its back wall is exposed to discharge pressure.
13. To check the integrity of the casing of pump & to
check for leaks or defects.
14. API 610.
15. Net Positive Suction Head is the difference between
total head and the vapour pressure head at the suction of a pump
16. Low NPSH may result in cavitation. NPSH is needed to
keep the centrifugal pump filled with liquid and in order to avoid vapour
formation in the impeller.
17. NPSHa is the net positive suction head available to the
pump, and NPSHr is the net positive suction head required by the pump to avoid
problems such as cavitation. NPSHa must be greater than the NPSHr for a pump to
run properly.
18. For two geometrically similar pumps following equations
can be derived which are called affinity laws:
Q ∞ N Q
∞ D3
H ∞ N2
H ∞ D2
P ∞ N3 P
∞ D5
where Q is flow, H is head, P is power, N is speed, D is
diameter
19. Different types of impellers are
Closed impellers : shrouds or sidewalls enclosing vanes
Open impellers : no shrouds or walls to enclose vanes
Partially open : shroud only on one side of vanes
20. Plunger type, lobe type reciprocating, diaphragm type
pumps
21. The effects of cavitation are drop in flow rate, damage
to impellers, high noise, high vibration.
22. Normal operating point on the pump curve at which the
flow the pump is currently operating at and rated point is the point at which
the pump is guaranteed to operate at
23. System resistance is the resistance offered to the flow
of the liquid by the system
If the system resistance increases then the flow rate
decreases and the pump operating point shifts and vice versa.
24.
25. Heavier fluid
26. Sealing in a centrifugal pump can be done either with
gland packing or with mechanical seals.
Gland packings are
generally used for a clean and cheap services such as quench water, fire water
etc.
Mechanical seals are
used where liquid is flammable. Sour oil pumps, VGO, column bottoms etc
27. The primary sealing elements are the flat faces of
rotary component and stationary component.
The secondary sealing
elements are elastomeric o rings, PTFE wedge, gaskets.
28. Double mechanical seals are used where leakages to
atmosphere are not tolerated such as toxic fluids and fluid which autoignite at
atmospheric conditions or when environmental pollution is an issue.
Single seals are used for purposes where minor leakages to
atmosphere can be tolerated.
29. In case of toxic services double mechanical seals are
preferred with flushing plan 53.
30. The major seal flushing plans are
11, 21, 23, 32,
52, 53, 62 etc
31. The function of pumping ring is to pump back the liquid
from seal chamber to seal pot or reservoir. Pumping ring is used in plans 23,
52, 53
32. Therminol 66, Molykote L1605, diesel.
33. plans 21, 23
34. By observing cooler inlet and outlet temperatures.
35. Decreasing.
Labels: api 610, bearing, cavitation, centrifugal, epc-school, flushing plan, mechanical, NPSH, pumps, Rahul Kapoor, rotary, seal
Subscribe to Comments [Atom]

Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.